본문
Promoting engineering students' social responsibility and willingness to act on socioscientific issues

by Prof. Hyunju Lee
Department of Science Education
PURE Research Profile
hlee25@ewha.ac.kr
As Beck (1992) noted, we are living in a “risk society”, in which scientific and technological advances constantly create new forms of risks such as infectious diseases, exposure to dangerous chemicals, environmental pollution, sinkholes, and energy shortages. These risks involve socioscientific issues (SSIs), which refer to socially relevant, real-world scientific problems that often include an ethical component. Many scholars and educators have insisted that scientists and engineers should pay more attention to and feel responsible for these emerging risks and issues.
Despite increasing awareness of the importance of promoting the social responsibility of science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) professionals, few intervention programs have been developed to enhance the social responsibility of college students or adults in the STEM fields. In this study, we introduced a new instructional program, called ENACT and examined whether the program increased the social responsibility among safety engineering students (N=46) recruited from a university located in a southern metropolitan area of South Korea.
“ENACT” is an acronym referring to the five steps of students’ investigation (Engage in SSIs, Navigate SSIs, Anticipate consequences, Conduct scientific and engineering practices, and Take action; see Fig. 1 for the full model). The ENACT model depicts the learning process in which college students select and explore SSIs based on their own interests, autonomously perform scientific and engineering group projects spanning a semester and share the solutions to the SSIs with their communities.
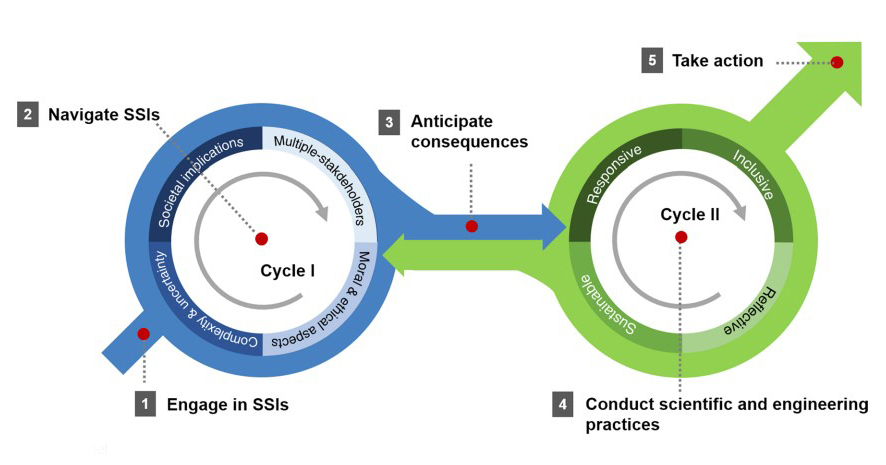
Figure. ENACT model
To measure students’ changing views of the social responsibility of scientists and engineers before and after the intervention, we used a scale called VSRoSE (Ko et al., 2023). VSRoSE reflects a broadened perspective on the social responsibility of scientists and engineers. The scale consists of thirty 5-point Likert-type scale items with eight factors: (1) concern for human welfare and safety; (2) concern for environmental sustainability; (3) consideration of societal risks and consequences; (4) consideration of societal needs and demands; (5) pursuit of the common good; (6) civic engagement and services; (7) communication with the public, and (8) participation in policy decision-making.
At the conclusion of the intervention in this study, the STEM students displayed an increased social responsibility regarding the consideration of societal needs and demands, civic engagement and services, and participation in policy decision-making. Social responsibility scores measured after the intervention (post-test) correlated with students’ willingness to voluntarily participate in projects involving SSIs. In addition, the intervention effects were more pronounced for the students who initially had medium and low social responsibility scores.
We have shown that social responsibility can be nurtured by systemic instructional approaches, and increased social responsibility can lead to greater commitment to resolving SSIs. Mastering engineering content knowledge and skills is the key element of engineering curricula. However, we are compelled to incorporate social responsibility into the STEM curriculum. We believe that the ENACT model contributes toward this end.
* Related Article
Yohan Hwang, Yeonjoo Ko, Sungok Serena Shim, Seung-Yong Ok, Hyunju Lee, Promoting engineering students' social responsibility and willingness to act on socioscientific issues, International Journal of STEM Education, vol 10, 1-16, February 2023
Yeonjoo Ko, Sungok Serena Shim, Hyunju Lee, Development and validation of a scale to measure views of social responsibility of scientists and engineers (VSRoSE), International Journal of Science and Mathematics Education, 21(1), 277-303, January 2023